Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence models and techniques that can create new content — such as text, images, music, video, code, and even 3D models — by learning from existing data. Unlike traditional AI, which primarily classifies, predicts, or detects patterns, generative AI generates outputs that resemble human-created content.
Generative AI uses machine learning models, particularly deep learning architectures like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and more recently, Transformer-based models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), to produce new data based on patterns learned from large datasets.
🧠 How It Works
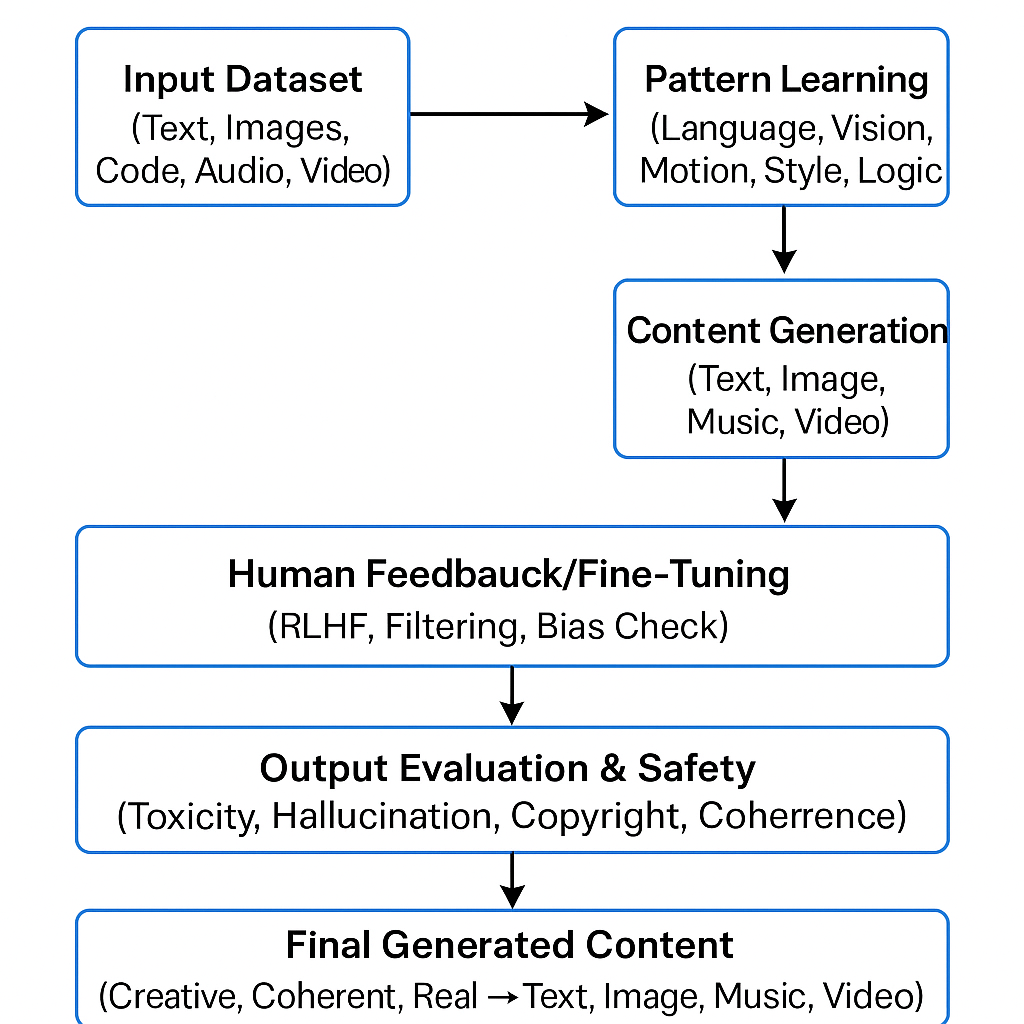
Fig: Working of GenAI
1. Input Dataset : Large volumes of data such as books, images, music, or code are collected :
- Text (books, articles, conversations)
- Images (art, photos)
- Code (from GitHub, etc.)
- Audio (music, speech)
- Video (YouTube, movies, surveillance)
2. Model Training : Generative Specialized models are trained for each modality:
- LLMs (e.g., GPT) for text/code
- Diffusion models (e.g., DALL·E, Sora) for images/videos
- GANs & VAEs for creative generation
- Video transformers (e.g., Sora, VideoPoet) for temporal learning
3. Pattern Learning : The model learns patterns, structures, and relationships in the data (e.g., sentence structure or visual styles).Models learn:
- Temporal dynamics for video (motion, transitions)
- Visual structures for images
- Acoustic features for music/audio
- Syntactic and semantic features for text/code
4. Content Generation: Using what it learned, the model can now generate new, original content — similar to human-created material
- Depending on prompts or context, the model can generate:
- Text (stories, articles)
- Images (illustrations, design)
- Music/Audio
- Videos (short clips, simulations, animated scenes)
5. Human Feedback / Fine-Tuning: In many systems, humans provide feedback to improve performance and alignment.
- Human-in-the-loop tuning improves:
- Accuracy
- Coherence (especially for video sequences)
- Ethical behavior (avoiding harmful or biased outputs)
6. Output Evaluation & Safety: Outputs are filtered for appropriateness, safety, accuracy, and bias before final use.
- Content is checked for:
- Toxicity, hallucination, misinformation
- Bias, plagiarism, or deepfake misuse (especially with video)
7. Final Generated Content: The output can be creative (art), functional (code), or educational (textbook explanations), ready for real-world application.
- Deliverables include:
- Creative: AI-generated films, animations
- Educational: explainer videos, simulations
- Realistic: synthetic yet believable visual storytelling
📽️Note
- Video Generation involves:
- Temporal Coherence: Frames must be consistent over time.
- Scene Understanding: Correct object behavior and physics.
- Multimodal Synchronization: Text, audio, and visuals aligned.
- Popular Video Gen Models:
- Sora by OpenAI
- Runway Gen-2
- VideoCrafter, Pika, Lumiere
🧰 Popular Generative AI Models
| Model Type | Examples | Output |
|---|---|---|
| LLMs (Large Language Models) | GPT-4, Claude, LLaMA | Text, code, dialogue |
| GANs | StyleGAN, BigGAN | Images, art, faces |
| Diffusion Models | DALL·E, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion | High-quality images |
| Audio Models | Jukebox, MusicLM | Music and sound synthesis |
✨ Applications of Generative AI
- Writing & Content Creation: Blog posts, scripts, novels.
- Art & Design: AI-generated illustrations, logos.
- Education & Tutoring: AI that explains concepts or generates test papers.
- Gaming: Creating virtual worlds, characters, and dialogue.
- Healthcare: Drug molecule generation, synthetic medical data.
- Engineering: CAD design generation, code completion.
⚖️ Benefits vs Challenges
✅ Benefits:
- Accelerates creativity and productivity.
- Enables rapid prototyping and innovation.
- Reduces time and cost for content generation.
⚠️ Challenges:
- Ethical concerns (plagiarism, misinformation).
- Biases in generated content.
- Ownership and copyright issues.
- High compute and resource costs.
🧩 In Summary
Generative AI is the branch of AI that doesn’t just analyze, it creates. It mimics the human ability to generate new ideas, designs, and narratives — transforming industries like media, design, healthcare, and education.