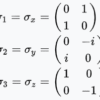Understanding the Needs of Undergraduate Students in Today’s World
Undergraduate (UG) education marks one of the most crucial phases in a student’s academic and personal journey. It is during these years that students transition from guided schooling to independent learning, self-discovery, and career preparation. The world today demands more from students than ever before—strong academics, interdisciplinary skills, emotional resilience, digital fluency, and societal awareness.
To support this transformation effectively, educators, academic institutions, parents, and policymakers must understand the core needs of UG students. These needs span across academic, professional, emotional, and social dimensions, all of which shape their readiness to navigate the modern world.
This article explores these needs in five comprehensive categories, offering insights valuable for faculty, administrators, and education designers.
Three Tiny 2×2 Matrices That Explain How a Qubit Feels the World
In the quantum world, the tiniest mathematical objects can reveal the deepest truths about reality.
The Pauli matrices — just three little 2×2 grids of numbers — are among the most powerful tools in quantum mechanics.
They form the mathematical DNA of a qubit, describing how it spins, flips, and rotates in its invisible quantum universe.
Understanding these matrices means understanding how a qubit “feels” directions in space — how it responds to measurements, gates, and the fundamental laws that govern quantum information.
Agentic AI: Where Intelligence Learns to Act
The world has been dazzled by Generative AI — systems that write, draw, compose, and code. But a quiet revolution is already reshaping the boundaries of machine intelligence.
This next frontier is Agentic AI — intelligence that not only generates but acts with intention, adapts through experience, and pursues goals autonomously. If Generative AI is about creativity, Agentic AI is about capability.
It doesn’t just answer or create; it plans, reasons, executes, and evolves.
This marks the beginning of a world where AI systems move from being “assistants” to becoming “collaborative partners.”
Synthetic Artificial Intelligence
The term Synthetic Artificial Intelligence (SI) is emerging as a transformative concept that extends beyond traditional Artificial Intelligence (AI).
While AI systems simulate aspects of human cognition using data-driven learning models, Synthetic AI aims to construct intelligence as an independent and self-evolving entity — a synthesis of perception, cognition, and action generated by machines themselves.
In simple terms, AI imitates human intelligence, whereas Synthetic AI creates its own version of intelligence. It represents a paradigm shift from learning from data to creating both data and intelligence.
Integrating Agentic AI and Quantum AI for Real-Time Problem Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of intelligent systems, two transformative paradigms—Agentic Artificial Intelligence (Agentic AI) and Quantum Artificial Intelligence (Quantum AI)—are emerging as complementary forces. Agentic AI brings autonomous, goal-driven behavior inspired by human-like reasoning, while Quantum AI harnesses the computational power of quantum mechanics to transcend classical computational limits. When integrated, these two can enable real-time intelligent decision-making, adaptive problem-solving, and scalable optimization in domains ranging from healthcare and finance to climate modeling and autonomous systems. This article explores the conceptual foundations, integration mechanisms, architecture, and practical applications of Agentic-Quantum AI synergy.