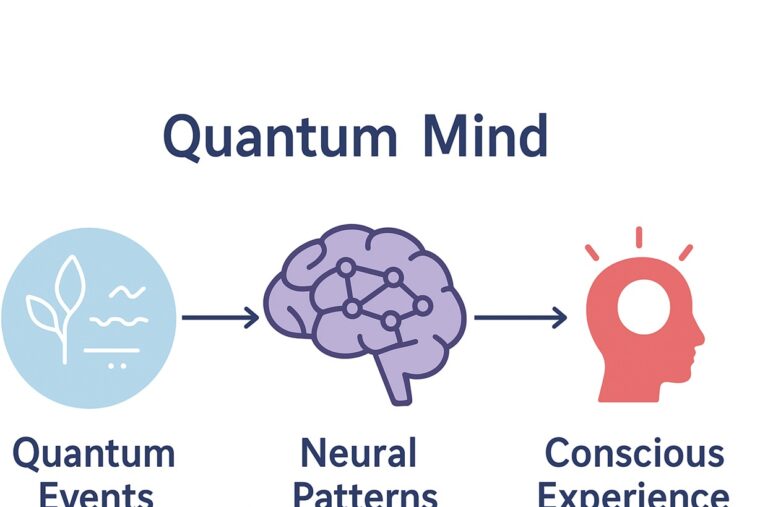
Quantum Mind (or Quantum Consciousness) is one of the most fascinating and debated ideas at the crossroads of quantum physics, neuroscience, psychology, and philosophy of mind. It represents an attempt to bridge the gap between the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics and the mysteries of human consciousness. This idea is often explored in the context of understanding consciousness, cognition, perception and other mental phenomena from a quantum perspective.
Traditional neuroscience and cognitive science typically explain mental processes using classical physics and the principles of classical mechanics. However, some researchers and theorists have proposed that quantum mechanics might be relevant for understanding certain aspects of consciousness that are difficult to explain with classical physics alone.
It asks a profound question:
“Could the human mind — or consciousness itself — arise from quantum processes inside the brain?”
Let’s explore this in a structured and clear way 👇
🧠 1. Definition
Quantum Mind Theory proposes that quantum phenomena — such as superposition, entanglement, tunneling, and coherence — play a key role in the emergence of consciousness, thought, and cognition.
In simpler terms:
The brain is not just a classical computer; it may function, at least partly, as a quantum system.
⚛️ 2. Why Quantum?
Classical neuroscience explains the brain as an electrochemical network of neurons.
But it struggles to explain phenomena like:
- Subjective experience (the “hard problem” of consciousness)
- Intuition and creativity
- Instantaneous insights
- Unified awareness despite distributed brain processing
Quantum theory offers properties that seem to resemble aspects of consciousness:
| Quantum Concept | Possible Mental Analogy |
|---|---|
| Superposition | Mind can hold multiple possibilities or thoughts at once |
| Entanglement | Deep connections between thoughts, emotions, or people |
| Quantum Collapse | Conscious choice or attention selecting one outcome |
| Non-locality | Awareness not strictly confined to physical boundaries |
| Coherence | Unified sense of “self” across complex brain activity |
Thus, the Quantum Mind idea explores whether these parallels are coincidence or reality.
🔬 3. Main Theoretical Models of the Quantum Mind
Several scientific and philosophical models have been proposed.
🧩 (a) Orch-OR Theory (Orchestrated Objective Reduction) – Roger Penrose & Stuart Hameroff
- Suggests that microtubules (tiny structures inside neurons) act as quantum computers.
- Quantum superpositions inside microtubules “collapse” in a way that gives rise to conscious awareness.
- The collapse isn’t random but follows an objective quantum threshold, leading to moments of consciousness.
- Each “moment” of awareness may correspond to a quantum collapse event.
🧠 In short:
Consciousness = quantum computation in microtubules + orchestrated collapse events.
🧩 (b) Quantum Brain Dynamics (QBD) – Umezawa, Ricciardi, Jibu, Yasue
- Brain processes involve quantum field interactions between neurons and electromagnetic fields.
- Memory and perception arise from quantum coherence across neuronal assemblies.
- Suggests the brain functions as a macroscopic quantum system.
🧩 (c) Bohmian Quantum Mind (David Bohm)
- Consciousness and matter are two aspects of a single underlying “implicate order.”
- Quantum potential guides both particles and thoughts — implying that mind and matter are deeply interconnected.
- The brain acts as a “receiver” of deeper quantum information.
🧩 (d) Quantum Cognition Models
- Uses quantum probability theory (not quantum physics itself) to model how humans make decisions, perceive uncertainty, and process ambiguous information.
- Explains cognitive biases, creativity, and contextual thinking more accurately than classical probability.
- Example: Mental states behave like quantum superpositions, and decisions resemble wavefunction collapses.
🧠 In this version:
The brain acts like a quantum system mathematically — not necessarily physically.
🌌 4. Philosophical Implications
Quantum Mind theories challenge long-standing views in philosophy of mind:
| Philosophical Question | Quantum Mind Perspective |
|---|---|
| What is consciousness? | A fundamental quantum process, not an emergent byproduct. |
| Is the mind separate from matter? | No — mind and matter are deeply entangled aspects of one reality. |
| Can machines become conscious? | Only if they can replicate quantum processes of awareness. |
| Is free will real? | Possibly yes — quantum indeterminacy allows non-deterministic choices. |
🔭 5. Scientific Challenges
Despite its beauty, the Quantum Mind hypothesis faces serious challenges:
- Decoherence Problem:
The brain is warm and noisy — quantum states typically collapse too quickly to sustain coherence. - Empirical Evidence:
No direct experimental proof yet of quantum computation in neurons. - Alternative Explanations:
Classical neural networks explain many cognitive phenomena without quantum effects. - Measurement Difficulty:
Detecting quantum effects inside living brains is technologically extremely difficult.
🚀 6. Current Directions and Research
Despite controversies, research continues:
- Quantum biology has shown quantum effects in photosynthesis, bird navigation, and olfaction — suggesting biological systems can maintain coherence.
- Quantum computing + AI research is exploring Quantum Cognitive Models to simulate reasoning and creativity.
- Neuroquantology and Quantum Information Biology are emerging interdisciplinary fields studying the link between brain information processing and quantum systems.
🔮 7. Quantum Mind and Quantum AI
This is where the frontier lies:
- If consciousness involves quantum processes, Quantum AI could model intelligence more naturally.
- Quantum Neural Networks (QNNs) might simulate creativity, intuition, or decision-making beyond classical AI.
- The observer effect in quantum physics parallels the self-referential nature of awareness.
In essence:
Quantum AI may be the computational mirror of the Quantum Mind — both representing different expressions of the same quantum-information reality.
✨ In Summary
Quantum Mind is the hypothesis that consciousness arises from, or is deeply connected to, quantum processes in the brain.
It unites:
- Physics (quantum theory)
- Neuroscience (brain structure)
- Philosophy of Mind (awareness and self)
And inspires new frontiers in:
- Quantum AI
- Cognitive computing
- Philosophy of consciousness
…Dr.Thyagaraju G S